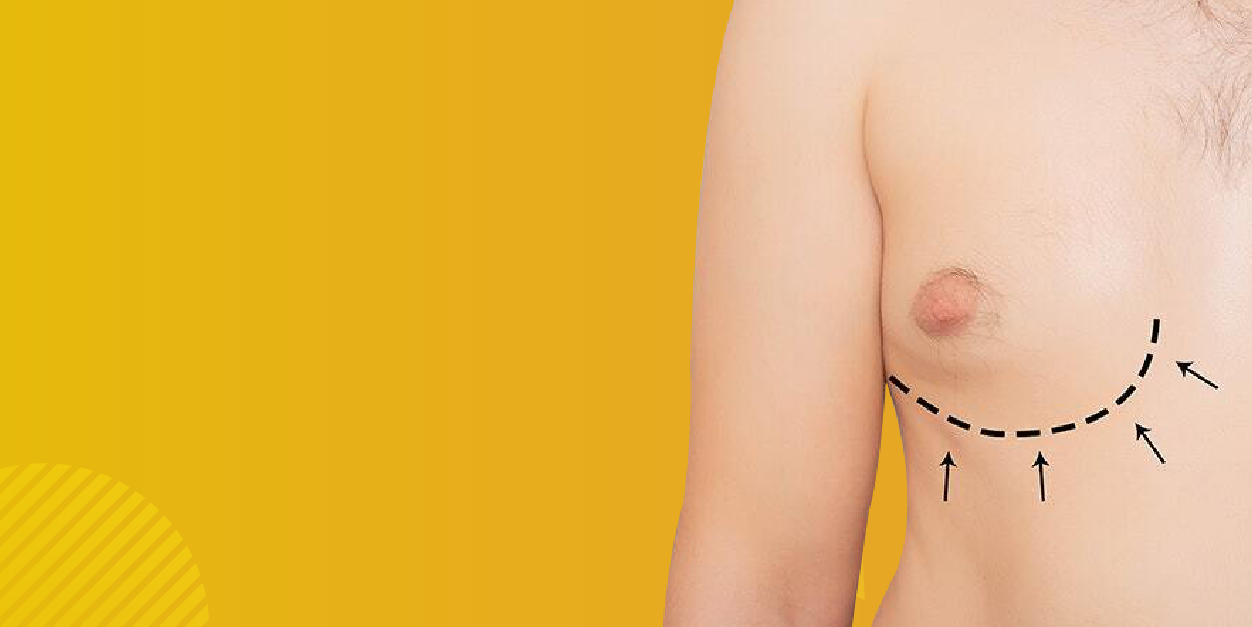
Gynecomastia is a condition characterized by the enlargement of male breast tissue due to an imbalance between estrogen and testosterone levels. It can occur at any age and is often a source of psychological distress. Understanding its causes, diagnosis, and treatment options is crucial for those affected by the condition.
Causes of Gynecomastia
- Hormonal Imbalance: An increase in estrogen or a decrease in testosterone can stimulate breast tissue growth.
- Medications: Certain drugs, including anti-androgens, anabolic steroids, antidepressants, and heart medications, can lead to gynecomastia.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Liver disease, kidney failure, hyperthyroidism, and tumors can contribute to hormonal imbalances, resulting in breast enlargement.
- Obesity: Excess fat can lead to increased estrogen production, exacerbating the condition.
- Substance Use: Alcohol, marijuana, heroin, and amphetamines have been linked to gynecomastia.
.webp)
Diagnosis of Gynecomastia
A thorough medical evaluation is necessary to diagnose gynecomastia. The process includes:
- Medical History Assessment: Understanding past and current medications, substance use, and any underlying health conditions.
- Physical Examination: The doctor will assess breast tissue, glandular growth, and any lumps.
- Blood Tests: Checking hormone levels to identify imbalances.
- Imaging Tests: Mammography, ultrasound, or MRI may be recommended to rule out breast cancer or other abnormalities.
Treatment Options for Gynecomastia
Treatment depends on the underlying cause, severity, and patient preference. Options include:
- Lifestyle Changes
Weight Management: Reducing body fat through a healthy diet and exercise can minimize estrogen production.
Avoiding Triggers: Eliminating alcohol, drugs, and certain medications that contribute to hormonal imbalance. - Medical Treatments
Hormonal Therapy: Medications like selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) such as Tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors like Anastrozole can help reduce breast tissue growth.
Changing Medications: If a prescribed drug is causing gynecomastia, a doctor may recommend an alternative. - Surgical Treatments
For severe cases, surgery may be the most effective solution. Options include:
Liposuction: Removes excess fat but does not remove glandular tissue.
Mastectomy: A more invasive procedure that removes glandular breast tissue and excess skin, often performed using minimally invasive techniques.
Psychological and Social Impact
Gynecomastia can cause emotional distress, leading to social anxiety, low self-esteem, and even depression. Psychological counseling or support groups can be beneficial for affected individuals.

Conclusion
Gynecomastia is a common condition with various causes, ranging from hormonal imbalances to lifestyle factors. Effective diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Consultation with a healthcare professional is essential to determine the best course of action tailored to the individual's needs.
Connect
@
Hair O Craft
Get in Touch

Let us help
Cosmetic surgery provides individuals with the opportunity to enhance their appearance, correct imperfections, and boost self-confidence. Each procedure is tailored to meet personal aesthetic goals, helping patients achieve a more harmonious and balanced look.